Identify A Pest With Our Insect Library
Rats
The Norway Rat
is larger and potentially more damaging than house mice and other rodents. The female generally:
- lives up to five (5) years and
- produces five (5) litters of up to fourteen (14) pups per year
In addition to structural and food damages, they are well-known vectors of cryptosporidiosis, hemorrhagic fever, Q fever, and hantavirus.
Mice
The House Mouse
is one of the most common pests.
Females can:
- live from one (1) to three (3) years
- give birth to litters of three (3) to fourteen (14) young
- five (5) to ten (10) times per year.
They can do a considerable amount of damage structurally, burrowing, and chewing through wood, plastic, and insulation and electric wires, unfortunately causing fire hazards. Mice also destroy food supplies and containers, soiling them with urine and feces. Mice create unsanitary conditions. They can also be vectors for transmitting leptospirosis, typhus, Ricketts, and tularemia.
Mosquitos
A female mosquito will lay one hundred (100) to two hundred (200) eggs at a time in any untreated open water source, and a successful pair can create a population of thousands in a single season. Generally, the more open, stagnant water sources available, the more mosquitoes will be present. Mosquitoes are responsible for the rampant spread of diseases like yellow fever, dengue fever, equine encephalitis, West Nile virus, and, of course, malaria.
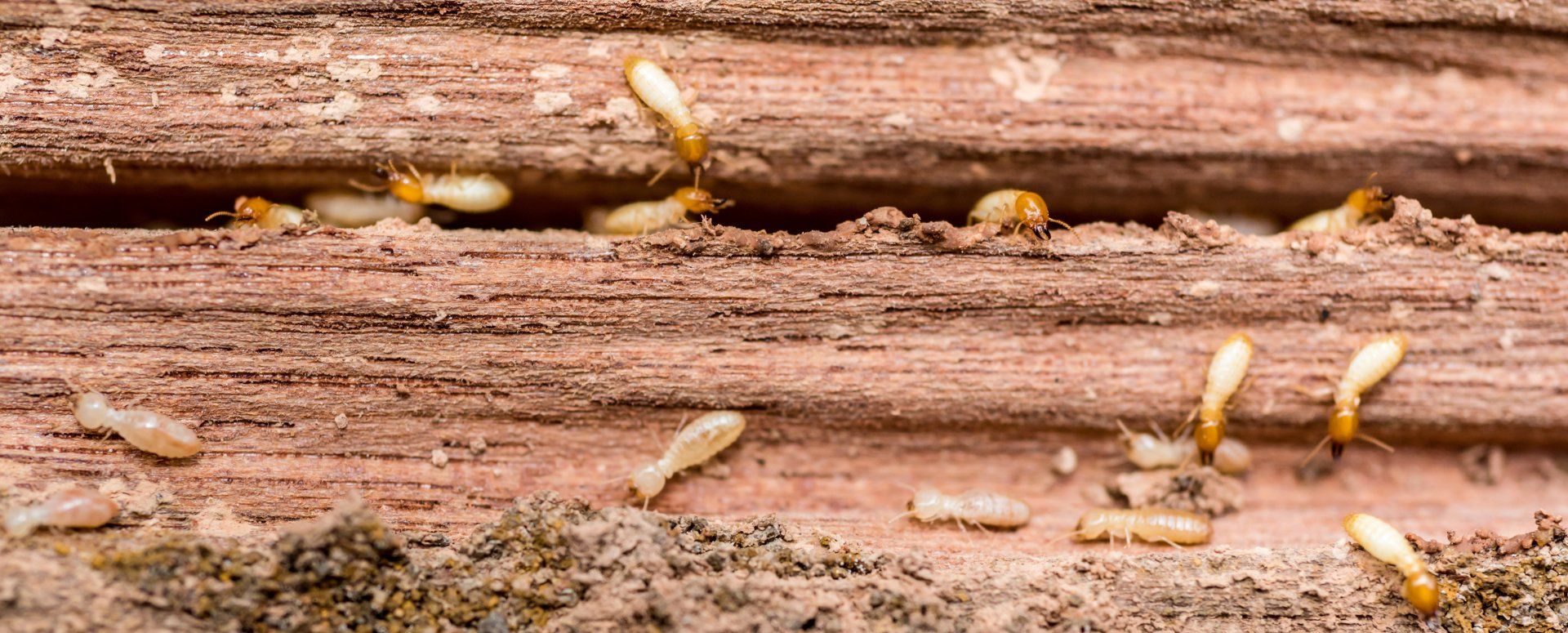
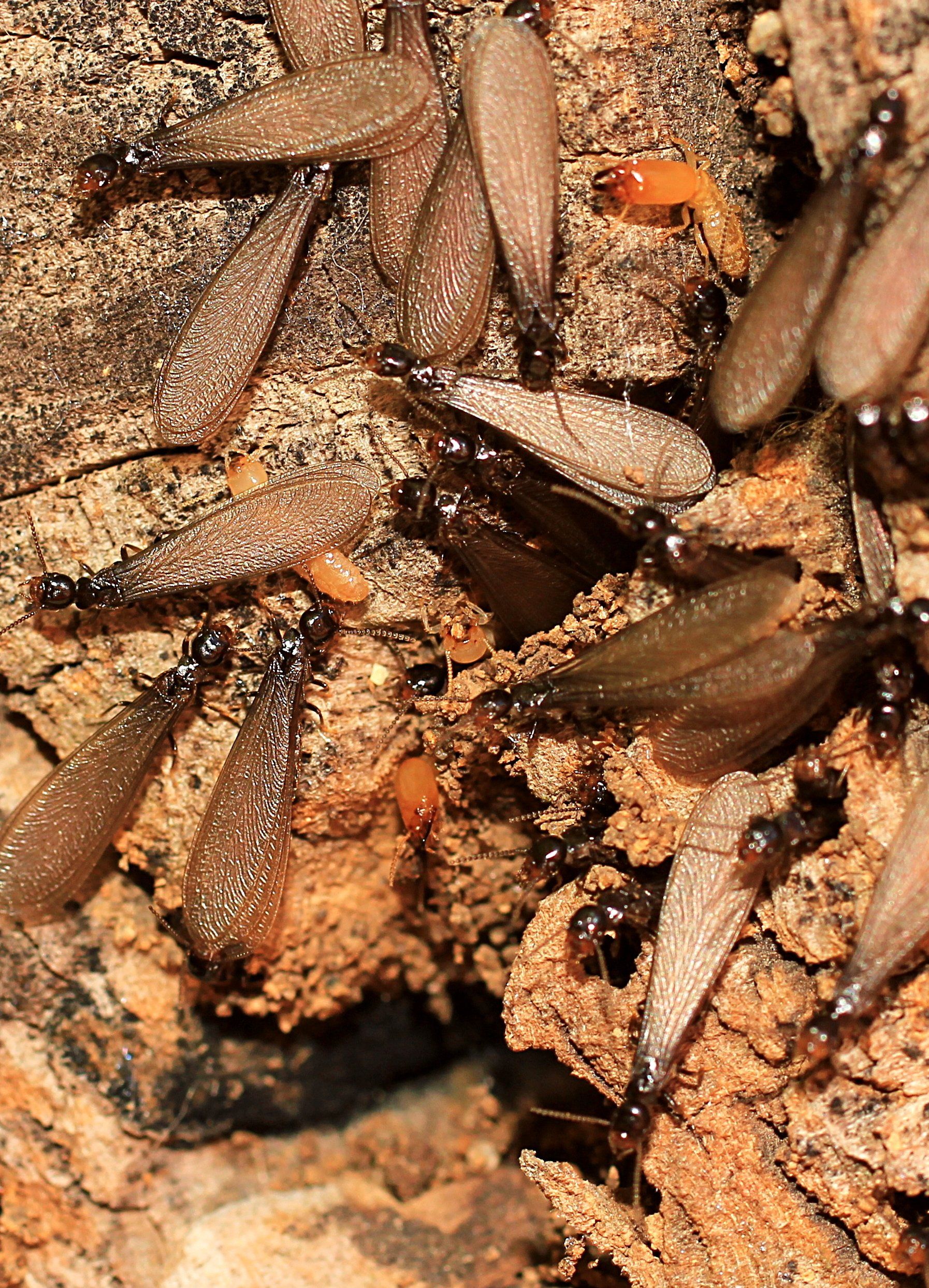
Termites
Termites are usually discovered when either their shelter tubes are found in wood or masonry or when a winged swarm emerges from infested wood. After swarming, they mate, land, and quickly remove their own wings, and sometimes these are the only signs that they are still present. Upon maturity, a single queen
from one of these swarms can produce 20,000-30,000 eggs per day
and live for several years. They feed on and burrow through wood or other cellulose-based products and cause untold structural and monetary damage every year.
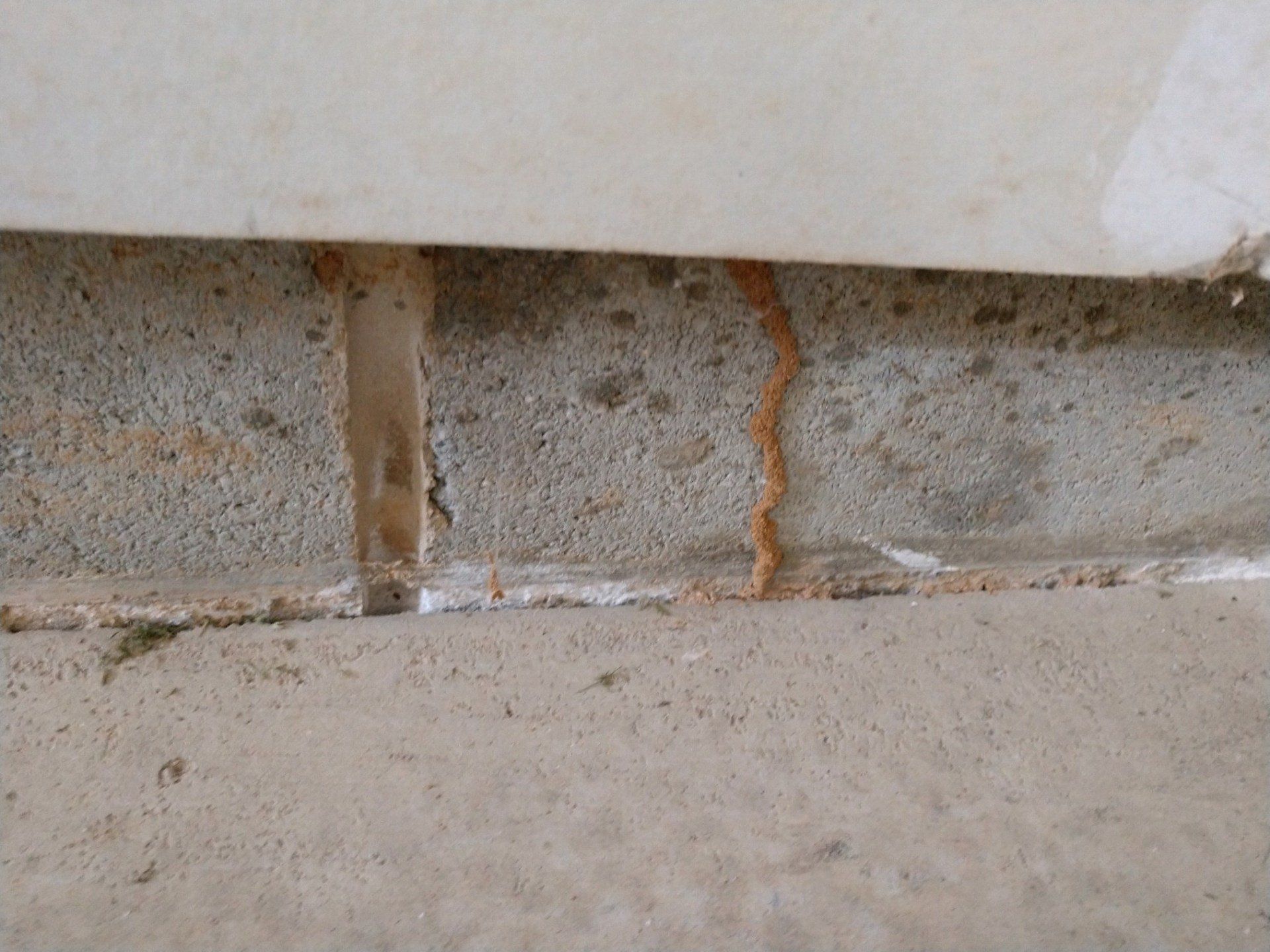
How Can I Tell If Termites Are Eating My House?
Ants
Many species of ants are happy to make their homes in ours. More than just a nuisance, they multiply quickly, form new colonies just as quickly, and can cause a great deal of damage both structurally (as with carpenter ants) as well as spoiling food and drink sources. Some are well known for their severe bites and stings.
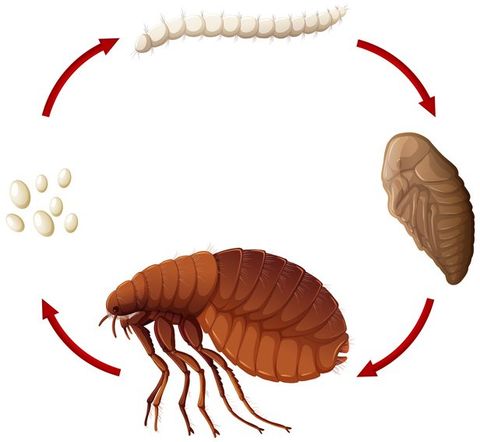
Fleas
Fleas can live as little as one year, but the female can produce up to five thousand (5000) eggs at that time. In addition to the sheer annoyance of insect bites and welts, they can also directly transmit Ricketts, typhus, and a variety of other bacterial and viral infections. In severe cases, infected animals can become anemic (low red blood cell count) from the loss of blood from feeding fleas.
Bedbugs
Bed bugs have made a serious resurgence in the last few decades in the United States. They can be found inhabiting mattresses, bed lines, couches, and furniture, anywhere that humans spend sufficient time at rest to allow their feeding. They live an average of nine (9) months and in that time can produce as many as five hundred (500) new bed bugs each. They are responsible for skin rashes and welts related to their bites, and, let's face it, they're just gross.
Millipedes
Millipedes are myriapods that have two pairs of legs on most body segments. Each double-legged section is a result of two single parts fused as one. Most millipedes have very elongated cylindrical bodies. Some millipedes are flat dorso-ventrally, while pill millipedes are shorter and can roll into a ball, like a pillbug.
Millipedes are detritivores and often slow-moving. Most millipedes eat decaying leaves and other dead plant matter, moisturizing the food with secretions and then scraping it in with their jaws. However, they can also be minor garden pests, especially in greenhouses, where they can cause severe damage to emergent seedlings. Signs of millipede damage include the stripping of the external layers of a young plant stem and irregular damage to leaves and plant apices, the very top of a plant.
Centipedes
Centipedes can have a varying number of legs from under 20 to over 300. A key trait uniting this group is a pair of venom claws or forcipules
formed from a modified first appendage. Centipedes usually have a drab coloration combining shades of brown and red. Centipedes range in size from a few millimeters to about 30 cm (12 in) in the largest scolopendromorphs. Centipedes are found in a wide variety of environments, from tropical rainforests to deserts. Within these habitats, centipedes require a moist micro-habitat because they don't have the waxy cuticle of insects and arachnids, and so lose water quickly through the skin. Accordingly, they are found in leaf litter and soil, under stones and dead wood, and inside logs.
Spiders
Spiders have eight legs, breathe air, and have fangs that inject venom. Spiders differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segments are fused into two tagmata, the cephalothorax, and stomach, and joined by a small, circular pedicel. Unlike insects, spiders do not have antennae. They can be found in air vents, corners of rooms, attics. They find quiet, hidden spaces where they can get food and water.
Crickets
Crickets are insects somewhat related to grasshoppers. They have slightly flattened bodies and long antennae. There are more than 900 species of crickets. They are typically nocturnal and are frequently confused with grasshoppers because they have a similar body shape, including jumping hind legs. Crickets do not harm humans.
Wasps
The term wasp
is defined as any insect of the order Hymenoptera and suborder Apocrita that is neither a bee nor an ant. Almost every pest insect species has at least one wasp species that preys upon it or parasitizes it, making wasps critically important in natural control of their numbers, or natural biocontrol. Parasitic wasps are increasingly used in agricultural pest control as they prey mostly on pest insects and have little impact on crops.
Yellow Jackets
Yellow jacket
is the official name for predatory wasps. Most of these are black and yellow; some are black and white. Others may have a red stomach background color instead of black. Yellow jackets have distinctive markings; they live in colonies and have a characteristic side to side flight pattern before landing. All females sting. Despite having drawn the hate of humans, yellow jackets are, in fact, essential predators of pest insects.
Hornets
Hornets
are the largest stinging pests. They are very similar in appearance to yellowjackets. Hornets eat insects and build aerial nests. Hornets are social insects. Hornets have reddish-brown heads and thoraxes, with abdomens that are golden with dark brown stripes. Hornets build nests by chewing wood into a paper-like pulp, by mixing it with their saliva. The nest is about the size of a basketball once it is fully built. If the nest is close to your home posing a threat, we can help.
Flies
Flies have a pair of flight wings on the mesothorax and a couple of halteres, derived from the hind wings, on the metathorax. The only other order of insects bearing two functional wings plus any form of halteres is the Strepsiptera. House flies are nuisance pests, and they can spread diseases.
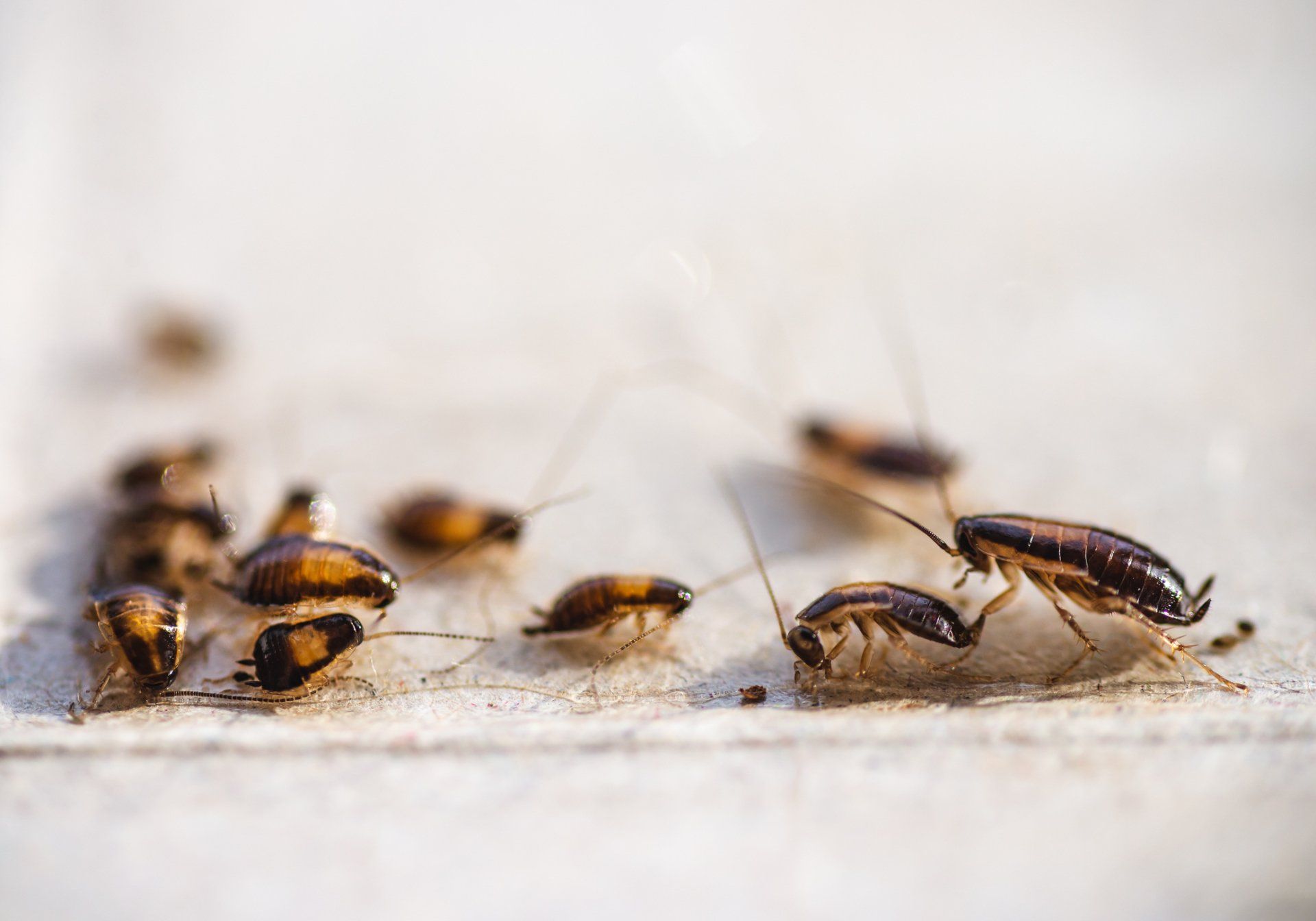
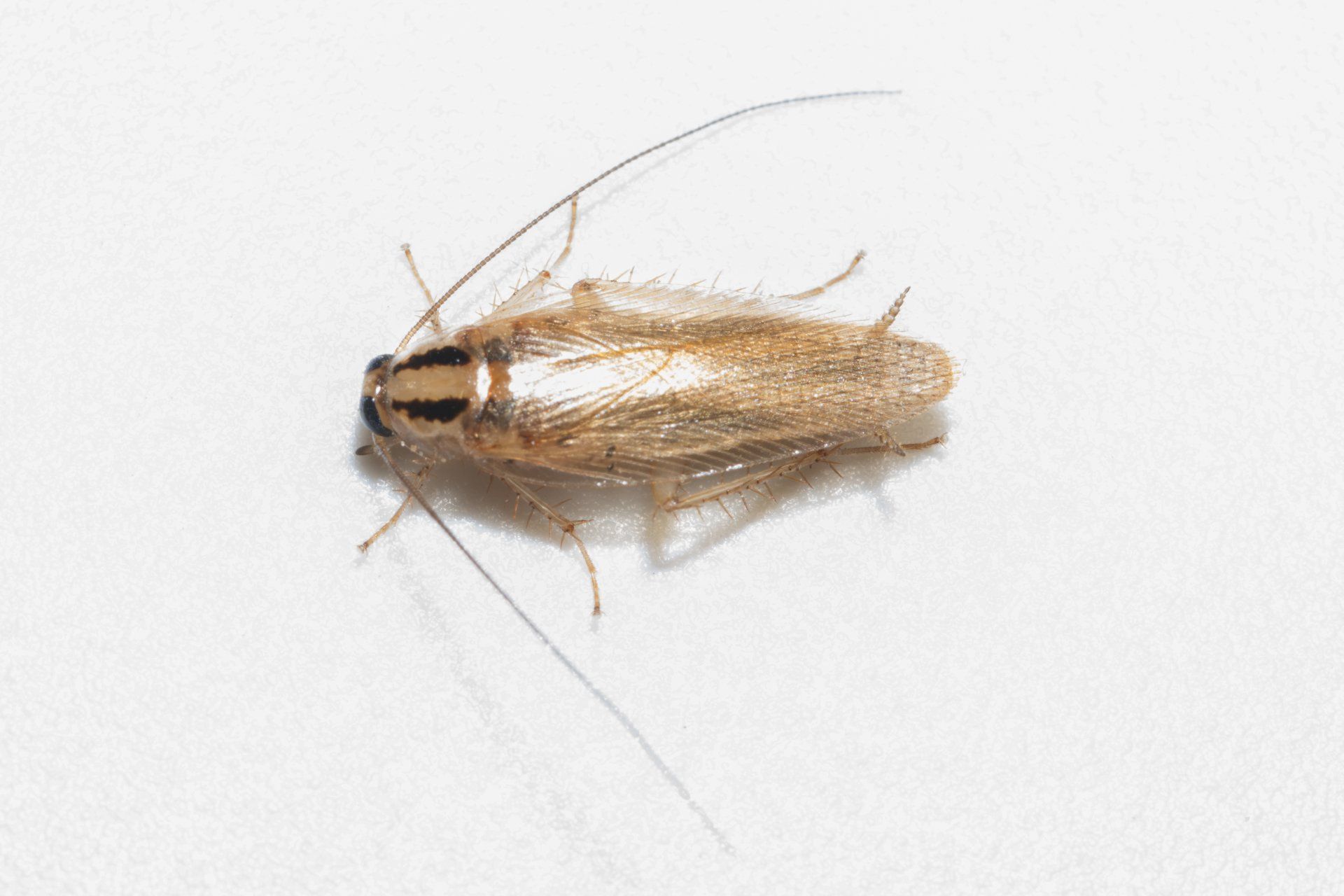
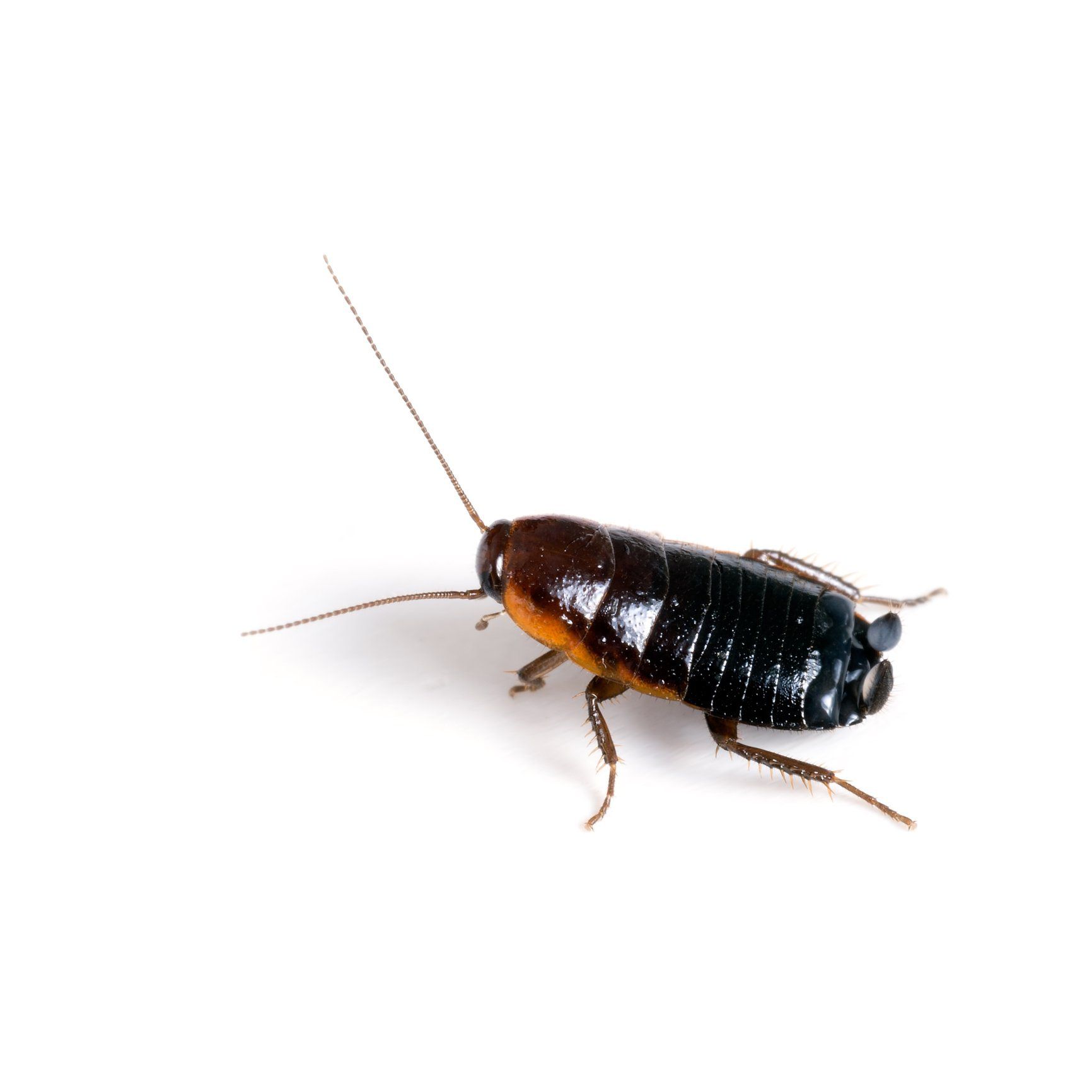
Roaches
Several species of roaches
infest and invade our homes, most commonly the Asian and German types. A female can produce thirty (30) to forty (40) eggs at a time and an average of three hundred (300) to four hundred (400) new cockroaches in her lifetime. The waste (urine and feces) they leave behind destroys food products that they invade as well as aggravating asthma and other allergic conditions.
Have questions about any of these insects or pests? Call us today at 302-650-6431
for more information.